
Bovine Anatomy Poster Cow Anatomical Laminated Chart
The pelvic canal, or birth canal, is where the fetus passes to exit the female reproductive tract. The pelvic inlet and outlet form the beginning and end of the birth canal, respectively. (Figs. 22.3, 29.3, 29.1) The pelvic inlet is the 'opening' at the cranial aspect of the pelvis, formed by pelvic bones and the sacrum.
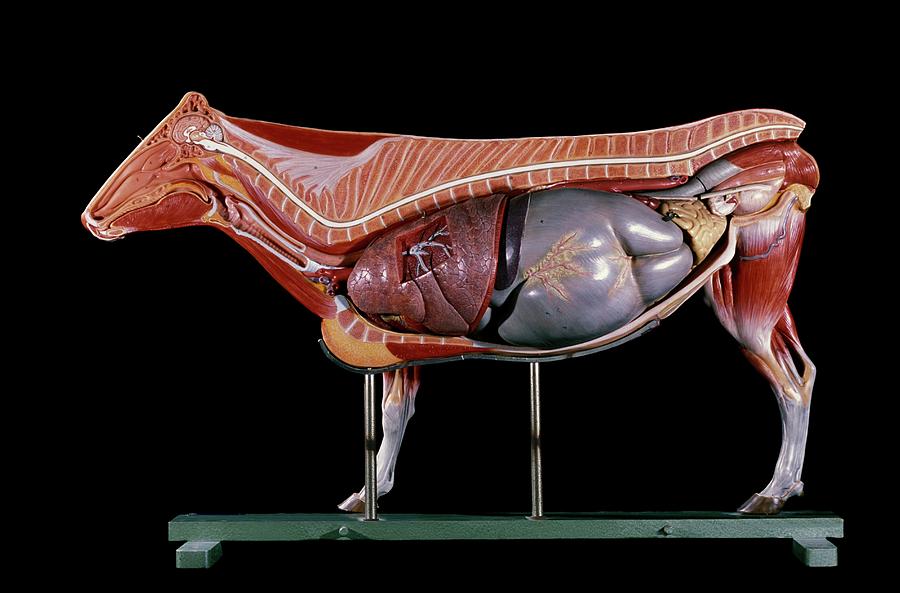
Anatomical Model Of A Cow Photograph by Patrick Landmann/science Photo
The ability of a cow or heifer to successfully mate, conceive, give birth, and raise a healthy calf each year is essential for profitable and sustainable beef production. A good understanding of anatomy and physiology of both the male and female is helpful in successfully managing reproduction.
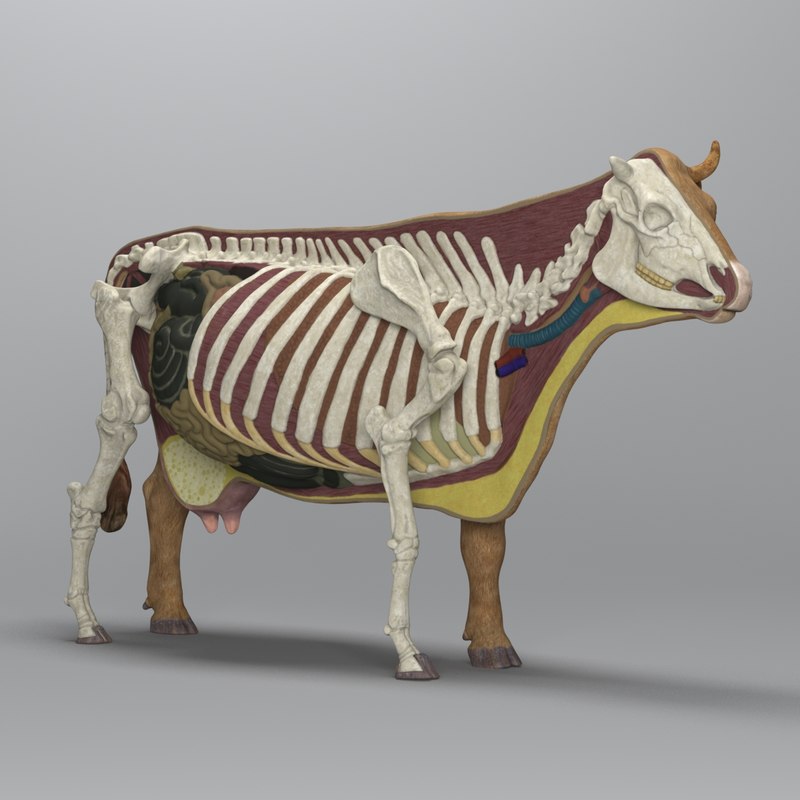
3d model of cow anatomy
11/5/2020 Successful artificial insemination programs are based on a clear understanding of the anatomy and physiology of reproduction in cattle. Before attempting to inseminate cows, you must develop a mental picture of the anatomical parts that comprise the female reproductive tract.

Cow Skeletal Internal Anatomy Veterinary Poster 18" X 24" Wall Chart
The cow's foot has only two functional toes, the much-enlarged nails of which comprise the hoof. As a result of its dual origin the hoof of the cow is in two parts and is said to be cloven. The 'shin' is formed by two metatarsals which are united to form one single bone. Cow musculature, digestive system, respiratory system and circulatory system.

Anatomia geral do touro e da vaca Atlas ilustrado
A group of cows, cattle, or kine (an archaic term for more than one cow) constitutes a herd. English lacks a gender-neutral singular form, and so "cow" is used for both female individuals and all domestic bovines. Britannica Quiz Match the Baby Animal to Its Mama Quiz

List Of Anatomy Of The Cow Ideas
The cow has the stomach volume and properties necessary to assist with the microbial digestion. The ruminant digestive tract and the ruminant stomach are shown in Figure 1. The ruminant stomach is divided into four compartments: the rumen, reticulum, omasum and abomasum. Digesta can flow freely between the first two compartments, the rumen and.

Atlas légendé d'anatomie générale bovine illustrations du taureau et
The cow stomach anatomy comprises four compartments - rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum. Here, I will focus on the anatomical facts of these four compartments of cow compound stomachs with a diagram. Quick overview: rumen is the larger and more capacious compartment than the reticulum, omasum, and abomasum of a cow's stomach.
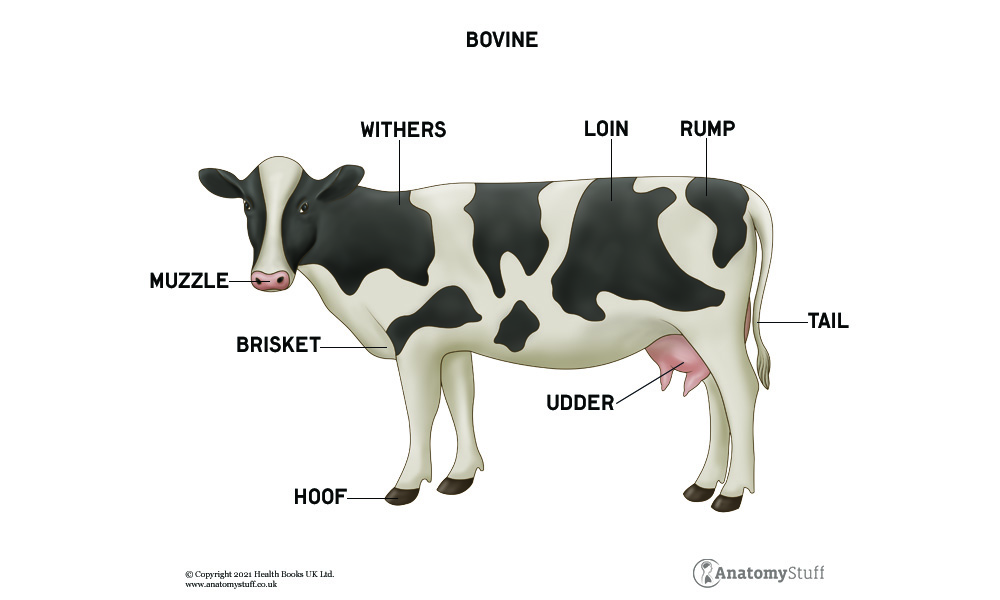
Cow Anatomy Bovine Muscles & Skeleton AnatomyStuff
Skin and Coat Unique Features Parts of A Cow | List Frequently Asked Questions Cows Let's start with the external body parts of a cow. A cow has many different parts, including the head, neck, legs, hooves, and tail. The head of a cow contains the mouth, nose, eyes, ears, and horns.

Parts of a Cow Useful Cow Anatomy with Pictures • 7ESL
Quick summary: the cow heart anatomy consists of 2 receiving (atria) and 2 discharging (ventricles) chambers internally. Externally the base and apex are more visible and covered by the serous pericardium. In addition, there are 2 distinct surfaces and 2 borders in the anatomy of a cow's heart.
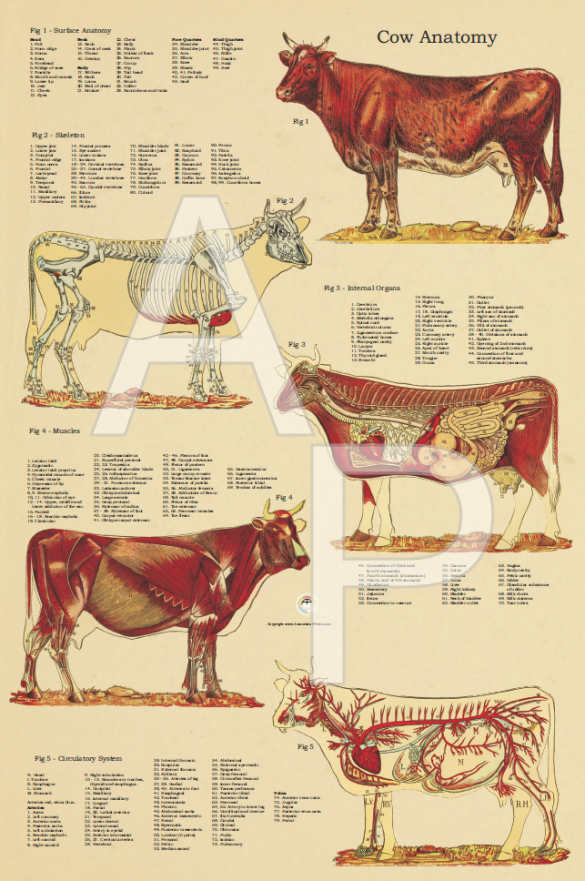
Vintage Anatomical Chart of the Cow 24 X 36
Bull-Cow - Sagittal section-Manus Bull-sagittal section of manus Bull-Cow - Terms of position and direction Bull-terms of position and direction ANATOMICAL PARTS Abaxial tendon Abdomen Abomasum Accessory carpal bone Acromion Adductor pollicis muscle Ala of ilium; Wing of ilium Anal region Antebrachial region

Pin on cattle health info
Parts of a Cow with Examples. Withers. Distance from withers to elbow and elbow to ground is equal. Back. The back of my neck throbbed painfully. Neck. Cats carry their kittens by the scruff of the neck. Ear. The dog was scratching at an itch behind its left ear.

Cow Ox Anatomy Poster Wall Chart 18 X 24 Etsy
Cow Anatomy Below is a diagram of the Anatomy of a Cow As you can see, there are many parts to a cow. Cows vary in all different colors, some are brown, tanned, white, black, brown-white patched or black-white patched. In a female cow, milk is produced in the udders and extracted from the teats.
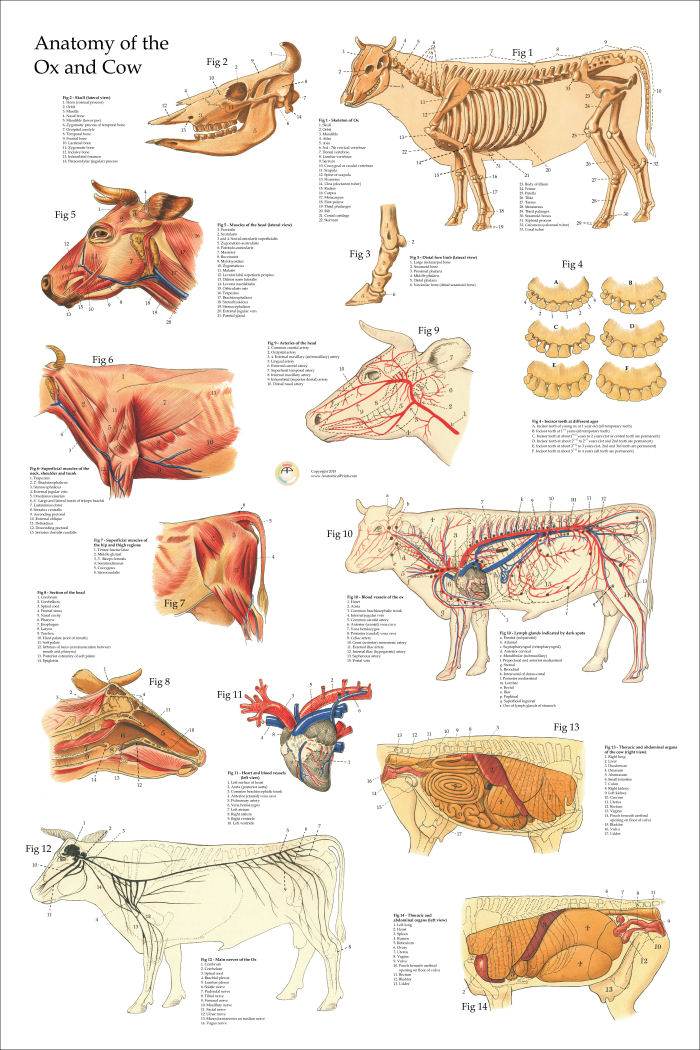
Anatomical Chart of the Ox Cow 24 X 36
The Four Compartments Rumen: The largest compartment, capable of holding up to 50 gallons of partially digested food. Reticulum: Known as the 'hardware' chamber, it aids in softening the food and also houses non-digestible items. Omasum: Here partially processed food, or 'cud', undergoes further processing.

Cow Anatomy Poster Clinical Charts and Supplies
The Cow Introduction Udder Anatomy Objectives This lesson with introduce you to the main structures of the bovine mammary gland (the udder). The mammary gland The mammary gland is an organ that all mammalian species have to nourish their new born young. The mammary gland of cows is called "udder." Supporting structures of the udder
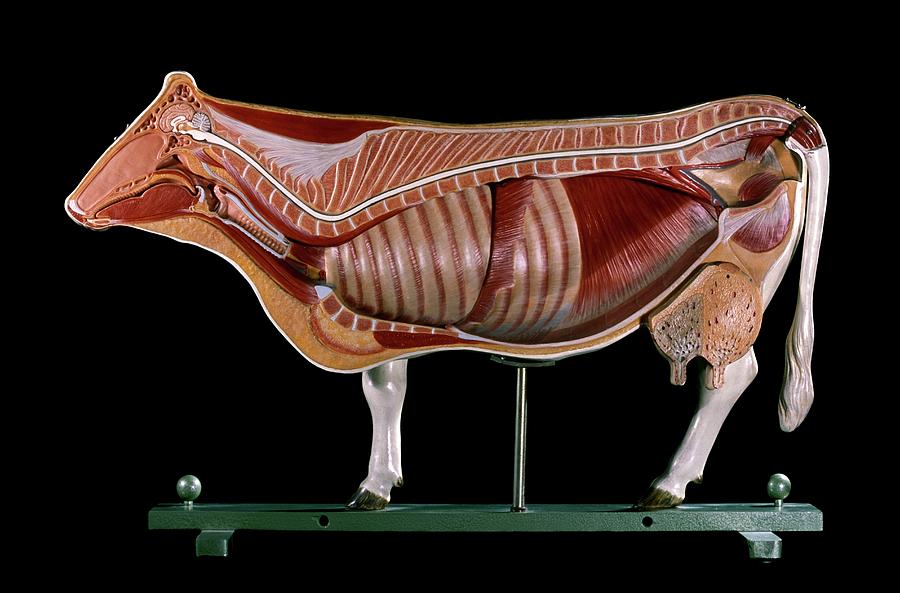
Anatomical Model Of A Cow Photograph by Patrick Landmann/science Photo
The vestibule (Fig. 1) is a part of the reproductive tract shared with the urinary system. It is approximately 4 inches long. Openings from the urinary bladder and a blind sac located below the opening of the urethra called the suburethral diverticulum are located on its floor.

Allgemeine Anatomie des Bullen und der Kuh Bildatlas
The cow muscle anatomy includes the study of their origin, insertion, fiber direction, and action. It is essential for veterinary students for further leaning of bovine anatomy. Here, I will help you to identify all the essential superficial muscles from the various regions of a cow with a labeled diagram.